Our abilities as humans to determine distance to an
object is a result of the brains process of visual
data. Both our eyes work in tandem to that any shift
from one eye to another allows for a determination
of distance. This is called parallax, or change in
an objects position based on the point of view of
the observer. The same effect works in
stars (that
are nearby only). This effect can be measured:
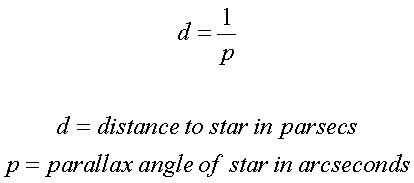
One of the nearby
stars is Barnard's Star. It has
a parallax angle of 0.547 arcseconds. To find the
distance:

Back to Top
|

