The Earth is composed of a solid inner core,
outer core, mantle, asthenosphere, lithosphere, and
crust.
| Name: |
Ingredients: |
Thickness: |
Temperature: |
| Inner Core |
Solid Iron and Nickel |
1230 km |
4300°
C |
| Outer Core |
Liquid Iron, Sulfur and
Nickel |
2250 km |
3700°
C |
| Mantle |
Plastic Magnesium, Iron,
Aluminum, Silicon and Oxygen |
2500 km |
1000°
C |
| Asthenosphere |
Elastic Mantle |
250 km |
1600°
C |
| Lithosphere |
Solid - Brittle Mantle |
100 km |
1400°
C |
| Crust |
Oxygen, Silicon, Aluminum,
Iron, Calcium, Magnesium, Sodium, Potassium,
Titanium, Hydrogen, Phosphorous, and trace
elements. |
Ocean: 8-10km
Continental: 10-70 km |
20°
C to 1400°
C (high temperature not a confident value) |
Convection is the engine driving the motions of
the lithosphere and crust.
The Earth is comprised of 14 rigid continental and
oceanic tectonic plates:
| Major Plates: |
Minor Plates: |
African Plate
Eurasian Plate
Australia Plate
Pacific Plate
Antarctic Plate
Nazca Plate
North American Plate
South American Plate |
Philippine Plate
Cocos Plate
Caribbean Plate
Scotia Plate
Arabian Plate
Indian Plate |
|
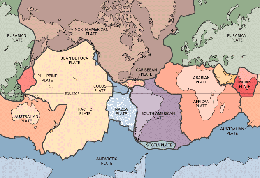 |
These plates "float" on
an "ocean" of hot magma called the
asthenosphere. Each plate contains a layer of crust
and a layer between the crust and asthenosphere
called the lithosphere.
Interactions
between these plates result in sea floor spreading,
earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain formation.
There are 5 types of tectonic movement: mid-ocean
ridge, oceanic plate meeting (example - Mt.
Pinatubo), diving plates (example - Andean
Mountains), sliding plates (example - San Andreas
Fault), and colliding plates (example - The Alps).
The shifting of these plates is such that there
are 7 major periods of continental drift:
| Cambrian Period |
570 to 510 million years ago |
| Devonian Period |
508 to 362 million years ago |
| Carboniferous Period |
362 to 270 million years ago |
| Triasic Period |
245 to 208 million years ago |
| Jurassic Period |
208 to 145 million years ago |
| Cretaceous Period |
145 - 65 million years ago |
| Tertiary Period |
65 to 2 million years ago |
There are three main categories of rock: igneous
rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks.
There are several methods of land shaping:
coastal waters, ground water, rivers, meanders,
deltas, drainage basins, and gullies.
There are 5 major oceans: the Pacific Ocean, the
Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Southern
Ocean, and the Arctic Ocean.
There are 12 biographical regions:
| Biome: |
Characteristic: |
Example: |
| The Polar Regions |
Permanent Ice Caps |
Antarctica |
| Tundra |
Desolate Regions - Long Winters and
Short Summers |
Siberia |
| Needle-Leaf Forest |
Mild Summers |
Northern Canada |
| Broad-Leaf Forest |
Northern Hemisphere - Seasonal
Variations |
Eastern North America,
Japan |
| Temperate Rain Forest |
Warm Climate - Wet Summers |
Southeast Asia |
| Desert |
Very Dry - Little Rain |
Yuma, Arizona |
| Mediterranean |
Hot and Dry Summers - Short
Winters |
Spain, Italy |
| Tropical and Temperate Grasslands |
Large Regions - Seasonal Rains with
Alternate Droughts |
Argentina |
| Dry Woodlands |
Dry Trees and Shrubs |
South Africa |
| Tropical Rain Forest |
Year Around Warm Weather -
Large Quantities of Rain |
Belize |
| Mountains |
Vegetation Varieties |
The Rocky Mountains |
| Wetlands |
Tidal Flats, Marshes and Swamps -
High
Humidity |
Florida |
There are 8 types of natural hazards (with an
associated website):
The total population of Earth is around 5.5
billion people divided into 6 continental
categories:
| North America |
Varied Settlements |
| Europe |
Dense Settlements |
| South America |
Increasing Settlements |
| Africa |
Sparse Settlements |
| Asia |
60% of World's Population |
| Australia and Oceana |
Sparse Settlements |
Back to Top |

